Installation
Before the interactive DMS installer can be used to configure and deploy the DMS platform, a series of pre-requisite system checks and installation steps must be performed:
- Decide local vs server deployment
- Check system requirements
- Check other requirements
- Install Docker
- Install DMS executable
The sections below describe these tasks in detail.
Release Information
The table below lists the specific Overture service versions bundled with the current release of the DMS platform, including links to their release pages where you can download the latest versions and view their release notes:
| Service | Release # | Link to Releases & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DMS Installer | 1.0.0 | DMS Installer |
| Ego | Ego API 4.4.0 Ego UI 4.2.0 | Ego API Ego UI |
| Song | 4.5.0 | Song |
| Score | 5.3.0 | Score |
| Elasticsearch | 7.6.0 | Elasticsearch |
| Maestro | 3.8.0 | Maestro |
| Arranger | 2.12.3 | Arranger |
| DMS UI (Data Portal) | 1.0.1 | DMS UI |
 Finding the Latest Release on GitHub
Finding the Latest Release on GitHub
When viewing the GitHub release pages, multiple releases may be listed. If the list is large, the GitHub site may sometimes collapse the list. To make sure you can see the latest release, click Show X newer tags. This ensures the list is fully expanded and you can see the latest release.
Decide Local or Server Deployment
Before you perform any installation steps, you must first decide whether you want to deploy the DMS in local mode or server mode.
This decision is important because it will affect some of the pre-requisite setup tasks as well as later configuration tasks. Certain tasks will differ based on your choice. These differences will be clearly noted in the documentation as you proceed through the installation guide.
The DMS can be deployed to your cluster in one of two modes:
| Mode | Use Case | Access | Application Layer Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local | The purpose of local mode is to deploy and host the DMS only on a local machine's resources. For example, deploying to an individual user's laptop, or a private VM in the cloud. Local mode is typically used for solo users or small teams with shared access to a laptop or private VM. | Local host only | HTTP only |
| Server | The purpose of server mode is to deploy and host the DMS system using resources available on separate or external infrastructure from your local machine. For example, deploying to a VM on a cloud infrastructure, or your organization's internal IT infrastructure, etc. The intention of server mode is to make the DMS system available to external users, by exposing them via a configured domain name and securely over HTTPS. | Externally via custom domain name | HTTPS over TLS/SSL |
Your decision will depend on the following factors and you may need to consult with your IT department if you belong to an institution:
- Your desired use case
- Who will be accessing the DMS
- Your institution's available resources and IT infrastructure
- Security considerations
NOTE: Once the DMS has been deployed in a specific mode, it cannot be switched dynamically to use a different mode on-the-fly. For example, you cannot switch from local mode to server mode by simply updating your configuration. To re-deploy with a different mode, you must destroy your DMS cluster and restart fresh. For instructions on destroying your cluster, see here.
NOTE: The DMS currently only supports deployment to a single cluster. It is intended for use as a single node system and does not currently support high availaibility.
Check System Requirements
Once you have decided your deployment mode, check that the environment you will be deploying to meets the recommended system requirements.
Operating System
The DMS currently supports deployment to platforms running these operating systems:
- Linux
- MacOS (Intel Based)
 Apple Silicon Updates
Apple Silicon Updates
Our software is currently only compatible with Intel-based Macs, not Apple Silicon devices. We are actively working on updates to support Apple silicon. Thank you for your understanding.
Recommended System Requirements
| # CPU Cores | Memory | Disk Space |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 8 GB | 20 GB |
If your system does not meet the recommended requirements, you may need to upgrade to deploy the DMS. If you are part of an institution, you may need to consult with your IT department about acquiring the additional resources.
Check Other Requirements
After checking your system requirements, next you must also check that certain additional, ancillary requirements are also met.
Specifically, make sure of the following:
- You are comfortable and familiar using a command-line interface - Installation and configuration of the DMS and supporting software is largely done via command-line.
- You have SSH access to the environment you are deploying to - Specifically for deployments to remote servers, you will need to remotely access the server via SSH to perform certain operations.
- You have administrator
sudolevel permissions on the environment you are deploying to - Certain operations or programs may need to be run with you assuming the security privileges of another user (e.g. as an administrator).
- You have Bash shell 5.0.0 or up installed in your environment - DMS Installer commands are run in a Bash shell.
If you do not have SSH access, sudo capability, or Bash shell installed, you will need to acquire them. If you are part of an institution, you may need to consult with your IT department for support with these items.
Install Docker
Now that you have verified that your system meets all requirements, the next step is to install Docker to your environment.
All of the Overture services are packaged as docker images to be deployed and run as containers on the Docker platform. Hence, Docker installation is a mandatory requirement to use the DMS platform.
NOTE: For the DMS to function correctly on Docker, the Docker installation must be completed as instructed using the steps from the Docker documentation site itself. The DMS requires at minimum Docker Engine version 19.03.12 or up. See here for Docker versions and release notes.
Install Docker from Docker Docs
Log into your environment as an administrator and follow the instructions to install docker from the Docker documentation site here.
If you are running MacOS, follow the Docker Desktop for Mac instructions
If you are running Linux, select the instructions for your specific distribution from the Linux distribution table
Initialize the Docker Swarm Network
After successfully installing Docker, you must initialize the Docker Swarm network. The DMS platform uses Docker Swarm as a container orchestration tool and allows each container in the swarm to be accessed by Docker nodes within the same cluster.
To initialize the docker swarm network, from your command-line, enter:
$ docker swarm init
If successful, a message is displayed indicating the swarm was initialized and your current node is now a swarm manager:
Swarm initialized: current node (dxn1zf6l61qsb1josjja83ngz) is now a manager.
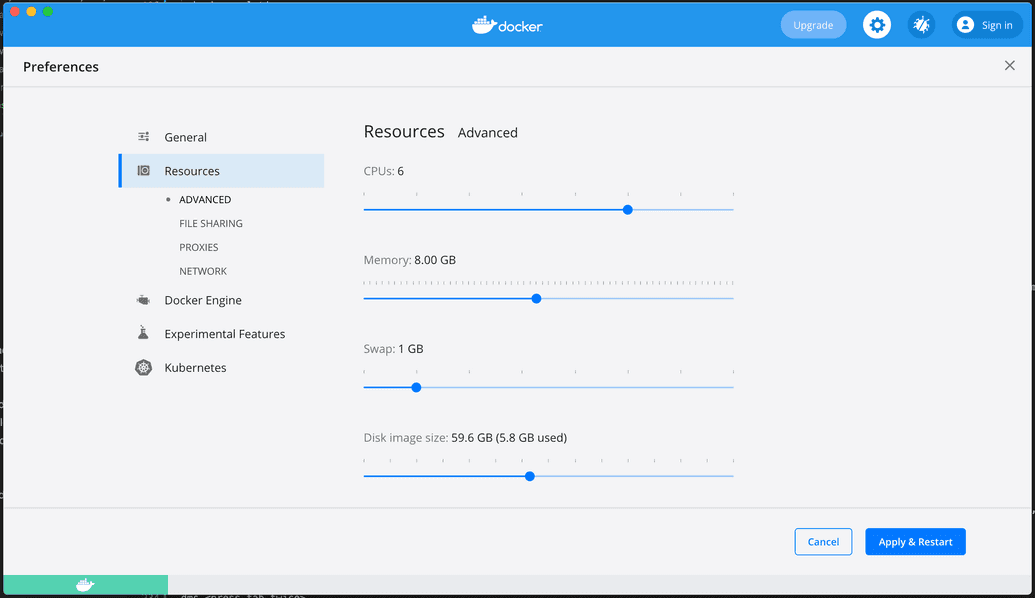
Adjust Docker Desktop Resource Settings (MacOS)
If you are running on MacOS, you need to check your Docker Desktop resource settings to ensure they are enabled for the recommended system requirements specified earlier.
- Open Docker Desktop and click Preferences.
- Go to Resources > Advanced.
- Adjust the number of CPUs and the amount of Memory to meet the recommended requirements.
- Click Apply & Restart.
Install the DMS Executable
The final installation step is to actually download and install the DMS executable.
Required Steps
- Log into your environment and open the command-line terminal.
- Download the latest version of the DMS installer executable, where
<x.y.z>is the version number:
$ curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/overture-stack/dms/<x.y.z>/src/main/bin/dms-docker > dms
- Make the file executable:
$ chmod +x dms
- Make the file usable from anywhere in your system:
$ sudo mv dms /usr/local/bin/
- Test that the executable works. This step serves two purposes: (1) To verify that the executable runs correctly and is not corrupted, and (2) To automatically generate the default
~/.dmsdirectory which is used to store some default configuration files. Type this command:
$ dms -h
This command simply lists the help menu for the DMS installer. If successful, the commands are listed:
$ dms -h____ __ ___ _____/ __ \ / |/ / / ___// / / / / /|_/ / \__ \/ /_/ / / / / / ___/ //_____/ /_/ /_/ /____/Installation Guide: https://overture.bio/documentation/dms/installation/User Guide: https://overture.bio/documentation/dms/user-guide/Usage: dms [-hV] [COMMAND]DMS command-h, --help Show this help message and exit.-V, --version Print version information and exit.Commands:config, cobuild, bu Interactively build a configurationget, g Get the current configurationcluster, clstart Deploy a configuration to the cluster.stop Stop a running cluster, without deleting data volumes.destroy Destroy the cluster and ALL the data.
- Check that the
~/.dmsdirectory was created by trying to switch to it:
ubuntu@sample-dms:~$ cd ~/.dmsubuntu@sample-dms:~/.dms$
If successful, the directory exists and you are able to switch to it.
Once the DMS executable is installed, you can now proceed to configure and deploy the DMS platform.
Optional Steps
Generate Bash Completion File
Optionally, you can generate a bash completion file, which improves usability of the DMS commands by allowing a user to autocomplete certain commands while typing.
- Generate the bash completion file:
$ dms bash-completion -n dms > ~/dms.bash_completion
- Load the bash completion file manually:
$ source ~/dms.bash_completion
NOTE: Currently, the bash completion file must be loaded manually. Hence, whenever you open a new terminal session to use the DMS, you will need to manually source the bash completion file again. However, you are free to automate this by adding the source command to your .bashrc file.
- Test the automcomplete functionality:
$ dms <press tab twice>
This displays a list of available top-level commands and their shortforms, if supported (e.g. "config" and "co"):
bash-completion cl cluster co config