Retrieving Data
Using Swagger
The Swagger UI is ideal for exploration and simple use cases. It will contain detailed descriptions of all the available endpoints, expected inputs, and error responses.
- Locate your endpoint of interest
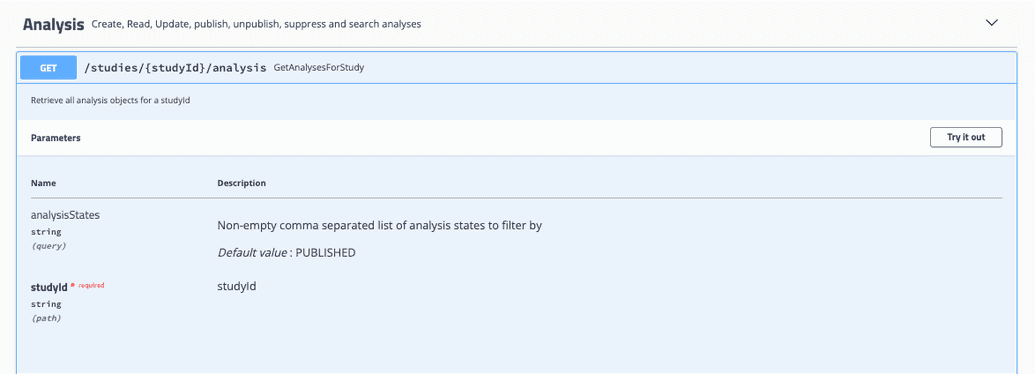
Any GET endpoint can be used to retrieve data from Song. For example, under the Analysis dropdown, you can find the GET GetAnalysesForStudy endpoint.
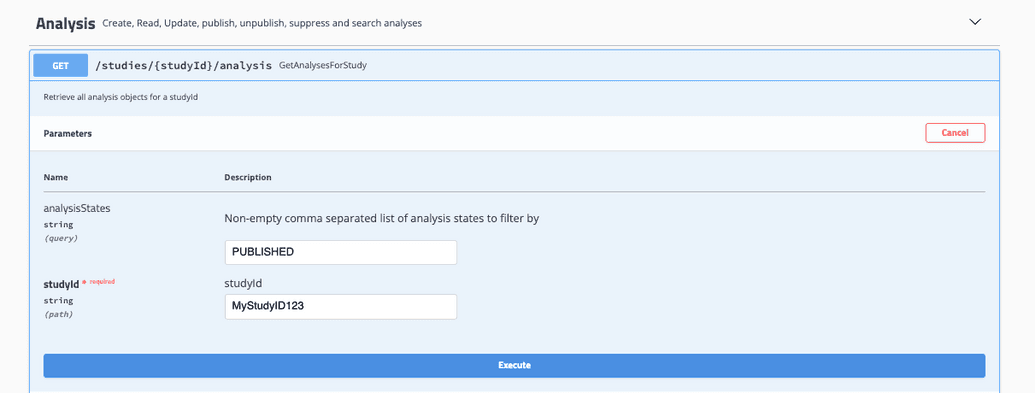
- Select Try it out and input your desired values
GetAnalysesForStudy takes in a studyID and analysis state and will return all associated analyses.
- Select Execute
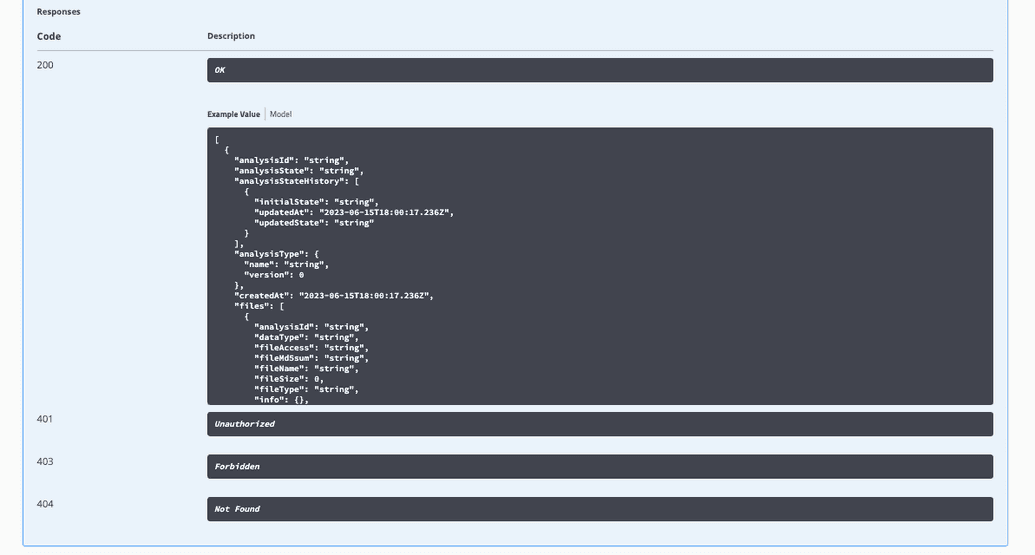
Expected responses, as well as response codes and descriptions, are conveniently documented within Swagger-UI.
Programmatic Queries
Here, we provide some examples of how to retrieve analyses using the Song API programmatically. If you have any questions or require technical support for your specific use case, please contact us on our Slack channel.
Example 1: Sample ID query
The following Python script performs a search for associated analyses based on a specific sample ID:
url="https://song.virusseq-dataportal.ca"sample="QC_546060"study="LSPQ-QC"endpoint="%s/studies/%s/analysis/search/id?submitterSampleId=%s) % (url,study,sample)response=requests.get(url)print(response.json()[0])
Example 2: Bulk analysis query
Analyses can be retrieved in bulk by using the GetAnalysesForStudy endpoint. This endpoint is only available in the most recent versions of Song and is currently unavailable within the DMS.
The following Python script demonstrates how to retrieve an aggregated list of published analyses and then create a filtered list of analyses associated to a series of submitterIDs.
import requestsimport pandas as pd### Declare bucket to house analysesaggregated_analyses=[]filtered_analyses=[]### Variablesstudy="MCPL-MB"status="PUBLISHED"url="https://song.virusseq-dataportal.ca"#Read CSV to identify specimenstmp=pd.read_csv("/Users/esu/Desktop/GitHub/virus-seq/2023_05_31/DP_Update_consensus_seq_version.csv",sep=",")#Cleaning up CSVtmp.set_index('Specimen Collector Sample ID',inplace=True)tmp['old']=tmp["Consensus Sequence Software Version(old)"]tmp['new']=tmp["Consensus Sequence Software Version(new)"]tmp.drop("Consensus Sequence Software Version(old)",axis=1,inplace=True)tmp.drop("Consensus Sequence Software Version(new)",axis=1,inplace=True)### First endpoint queryendpoint="%s/studies/%s/analysis/paginated?analysisStates=%s&limit=100&offset=0" % (url,study,status)response=requests.get(endpoint)### Check if query successfulif response.status_code!=200:print(response.status_code,endpoint)#sys.exit(1)### Endpoint returns a total that can be used downstream for analysis retrievaltotal=response.json()['totalAnalyses']### Append first set of analyses into bucketfor analysis in response.json()['analyses']:aggregated_analyses.append(analysis)### Return pages of 100 queries and append to bucketfor offset in range(100,total,100):endpoint="%s/studies/%s/analysis/paginated?analysisStates=%s&limit=100&offset=%s" % (url,study,status,str(offset))response=requests.get(endpoint)if offset%1000==0:print("Retrieving %s out of %s analyses" % (str(offset),(total)))if response.status_code!=200:print(response.status_code,endpoint)#sys.exit(1)for analysis in response.json()['analyses']:aggregated_analyses.append(analysis)### Filtering analyses according to sample specimen IDprint("Filtering analyses")for analysis in aggregated_analyses:if analysis['samples'][0]['submitterSampleId'] in tmp.index.values.tolist():filtered_analyses.append(analysis)print(len(aggregated_analyses))print(len(filtered_analyses))
 Tip
Tip
When making bulk calls, factor in time spent on API calls. For example, a data submitter who wants to retrieve 800/1000 analyses and only has submitter sample IDs can run 800 API calls for each submitter sample ID however a more efficient process would be to make bulk calls of 100 analyses (totalling 10 API calls) and then filtering accordingly for the desired submitter sample IDs.